Discovering a bump or lesion on your child’s scalp can be worrying, especially when a doctor isn’t immediately available. This guide offers a basic overview of common scalp issues so you can manage symptoms at home and decide when medical care is needed. The scalp can react to genetics, hygiene, environment, and infections. Conditions like seborrheic dermatitis often cause “greasy flakes and redness,” while folliculitis leads to “red, pus-filled bumps.” Because many problems look alike, understanding the differences helps you respond correctly.
Scalp bumps can come from dermatitis, infections, cysts, or chronic skin disorders. Pilar cysts are benign fluid-filled sacs that may grow larger. Psoriasis—a common autoimmune disorder—creates “thick, raised patches topped with silvery scales.” Knowing these possibilities can narrow down what you’re seeing.
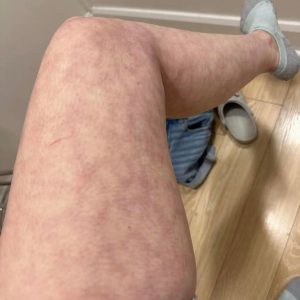
Psoriasis vulgaris is the most common type. It occurs when the immune system speeds up skin-cell growth, forming red, scaly plaques that may itch or crack. Flare-ups can be triggered by stress, cold weather, infections, or certain medications. Scalp psoriasis often appears as “well-defined reddish patches coated with silvery-white scales,” sometimes extending beyond the hairline and causing irritation or temporary hair thinning.
Simple home remedies may ease mild symptoms. Coconut oil, aloe vera, or diluted apple cider vinegar can soothe itching, while careful sunlight exposure may slow rapid skin-cell growth. OTC treatments like coal tar shampoos, salicylic acid, and mild corticosteroids can also help.
Seek medical care if symptoms worsen, don’t improve, interfere with daily life, or show infection signs such as spreading redness, pus, fever, or severe pain. Keeping notes and photos of symptoms—such as when they started and what triggers may be involved—helps your doctor make an accurate diagnosis.